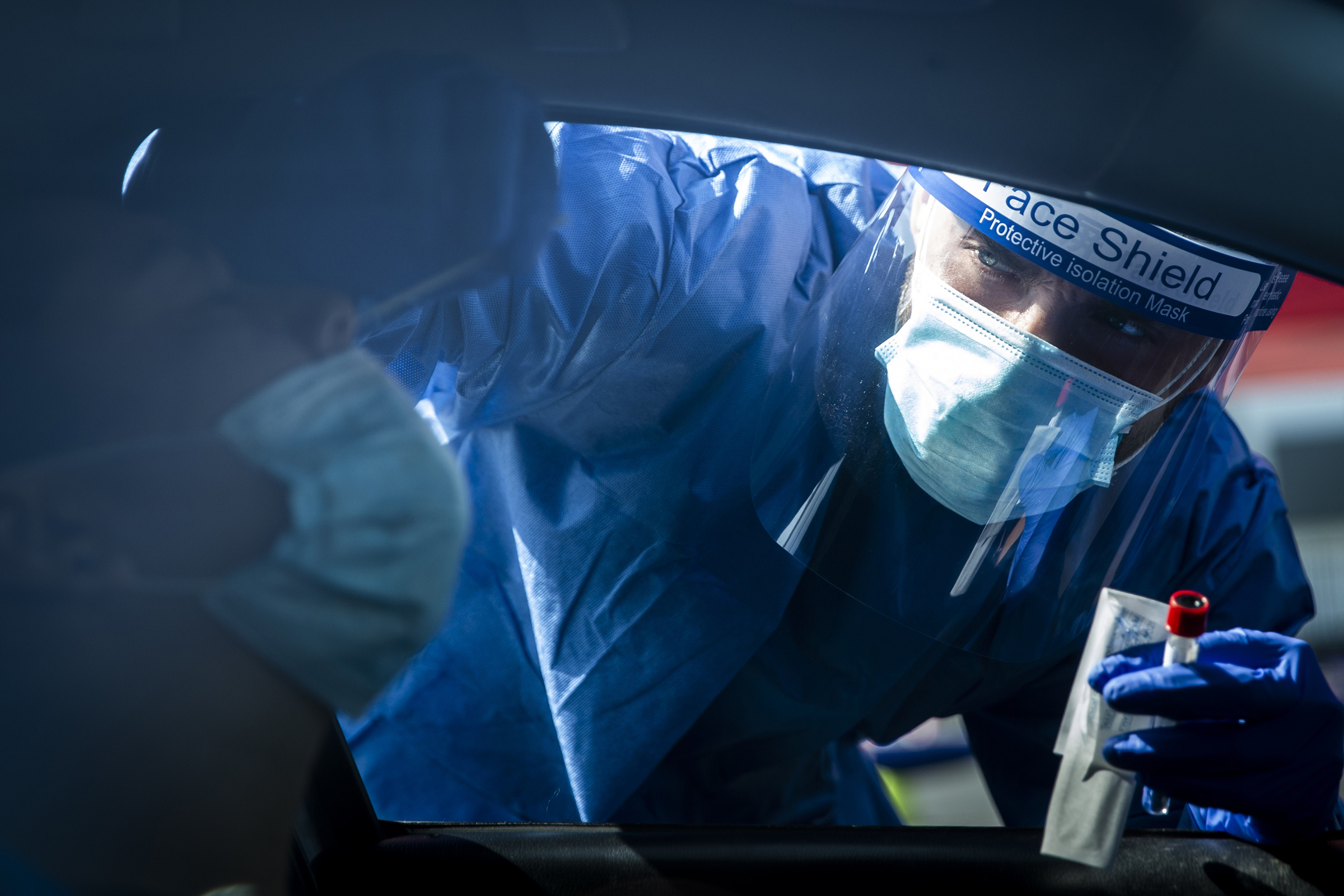
Countries around the world have strict COVID-19 introduced control measures is growing epidemics, but now many are at the bus stop in the same situation again. Melbourne to Miami, the relaxation of the measures had led to an increase of relapses, which in some places already schools, businesses, itineraries designed AWE. In the United States and between different countries, places with very different public health policy have experienced very different results. Most disturbing, infections are rising rapidly in many places where once were falling. Just as countries avoid a vague, untenable cycle of opening and closing of the company? What is needed to prevent a future of rigorous social distancing and closed borders? To escape this limbo, we need to know about each step of the chain of infection: why some people are more vulnerable or more symptoms, such as our interactions and environment affect risk and how to mitigate the effects of the resulting disease. Research around the world has led to these questions some promising ideas, but also some mixed results. Some studies suggest children are less susceptible to disease, while others suggest that they are less likely to spread the infection. There are indications that some aspects of immunity can wane quickly against the virus, while others persist. Based on specific records, few people actually are asymptomatic; according to other studies, a higher percentage can be. Often when a new disease outbreak, it turns out later exactly why it took the shape it did. In 1854 John Snow noted taking a cholera epidemic in the attack on the handle of a water pump in Soho in London. What happened next it is less well known: for the moment the handle is removed, the outbreak was already in decline. Since 1918 SARS pandemic influenza, history shows that many important insights arrive until long after the battle is over. Unfortunately, we do not have that luxury for COVID-19 In order to effectively and sustainably to control the disease, we need to better understand the infection that causes it. Since the 19-COVID pandemic has grown, so it has the apparent diversity varied with age and medical history of the impact of the disease on individuals, with the predisposition and severity. New medical findings could help reduce this diversity for the best. An effective vaccine could reduce vulnerability, to keep the infection from taking of arrest; an effective treatment would reduce the impact in the final stage of infection in the hospital, avoiding serious or fatal consequences. But to know what is truly effective, we need large clinical studies that can lay the first cases have decreased by hydroxychloroquine and dexamethasone processes in the UK, if we are not able to change the susceptibility or severity, then we have to see what happens in means: how people are exposed to the virus. This is the understanding of the range of the human environment that the transmission of drive. However, a patient should be treated with equivalent lockdowns all at once; something worked out, but it’s not entirely clear what. Schools and shops and bars and workplaces, every type of closure and our interactions changed, but transfer opportunities they create, we have to say, the data for certain that these changes in the most important. To prevent the successful execution the disorder, we need the variability of COVID-19-outbreaks and the control measures countries should be used to make more sense as the infection starts to spread and end. This variability has been damaged and unpredictable in the spring, but it should be in case, this same diversity could help us target the weaknesses in the infection process. As recognized in any source of noisy data explorer strongest signals about the risk before: Meatpacking factories, cruise ships, nursing homes. Countries such as Taiwan, Japan and South Korea have lockdowns untargeted partly prevented refine this knowledge necessary to collect data, they know where and how eruptions happen. There are indications that most of the people with COVID-19 uninfected anyone to spread the infection; even if the risk can not be completely avoided, intelligent structuring of interactions and superspreading life could limit events. Locations in different countries has introduced check-in flag Cluster thresholds to help as routine, rapid testing in the workplace blazes could help advance before they happen. Uncertainty about the risks can be translated into behavior, as we saw on the way in the block and see their way into uncertainty. The virus seems to be closed, especially in crowded, noisy and thrive long meetings. E ‘increasingly clear that a day at the park for an hour in a bar is very different. But the various dimensions of the transfer are often ignored in favor of a concentration on individual measures. Is six feet far enough? If masks are worn everywhere? Media reports show images of crowded beaches and parks, see the small transmission likely occurred while superspreading events in bars and workplaces. be relaxed as action, means uncertainty of unknowingly new agreement in hazardous environments you are heading, while others, the memories stay-at-home messaging environment must be avoided, which are now known to be relatively safe. While it may seem to provide local variation in uncertainty control measures, you can actually help to reduce, through intuition as fast as they are effective behavioral change. Take the introduction of protective mask requirements in Germany, where the various states turned over a period of 10 days. A problem with mandate facial mask use the introduction which could lead people to be complacent in their behavior. By staggering the time when the masks, Germany has created a natural experiment we were introduced ‘that could show what has happened on several sites. The results suggest that, if introduced mandatory masks States, has not resulted in visits to public places to a subsequent increase. There is not one, the data set to be perfect to be sustainable performance as the 19-COVID control If we want to reduce the susceptibility and severity or understand infection and immunity, we will learn from the diversity of the results and trends we see globally . This means of monitoring of infections from different directions, research studies established to monitor possible cases, and various data streams are interconnected monitoring systems. Since the second wave of the epidemic, many countries it is true, it is essential to gather the information needed to prevent a third party. Picture copyright by Alex Pantling-Getty Images
Related Post
COVID-19 is devastating even nursing homes. The administration Trump does not do much to stop it
At least 75,000 Americans in nursing homes and other structures have long-term care as soon as they died COVID-19 and the devastation is far from...
More than half of Americans fear that the pressure of the White House for a coronavirus vaccine will Rushed
For weeks, the US president Donald Trump has repeatedly forecasts, sometimes bordering on promises that a COVID-19 vaccine is imminent. "We remain on track to...
COVID-19 has killed nearly 200,000 Americans. How many more lives will be lost before the US makes it right?
Forty-five days before the announcement of the first suspected case of what the COVID-19 would be known, the global index of the Health Security has...
Nearly 2 million fewer US teens are vaping now than last year, the data show CDC
Nearly 2 million fewer US teens report on e-cigarettes in 2020 compared to 2019, according to new data from the US Centers for Disease Control...
The Great Race Vaccine: The unprecedented rush to immunize the world against COVID-19
The smarter enemies thrive on surprise attacks. Virus and crown in particular are well aware. remain hidden in animal hosts for decades, sometimes mutate constantly,...
Zeneca has taken its COVID-19 vaccine trial after a break for the security check
This story has been updated to reflect AstraZeneca's investigational vaccine shot. AstraZeneca, the British pharmaceutical company behind one of the most promising candidates COVID-19 vaccine...